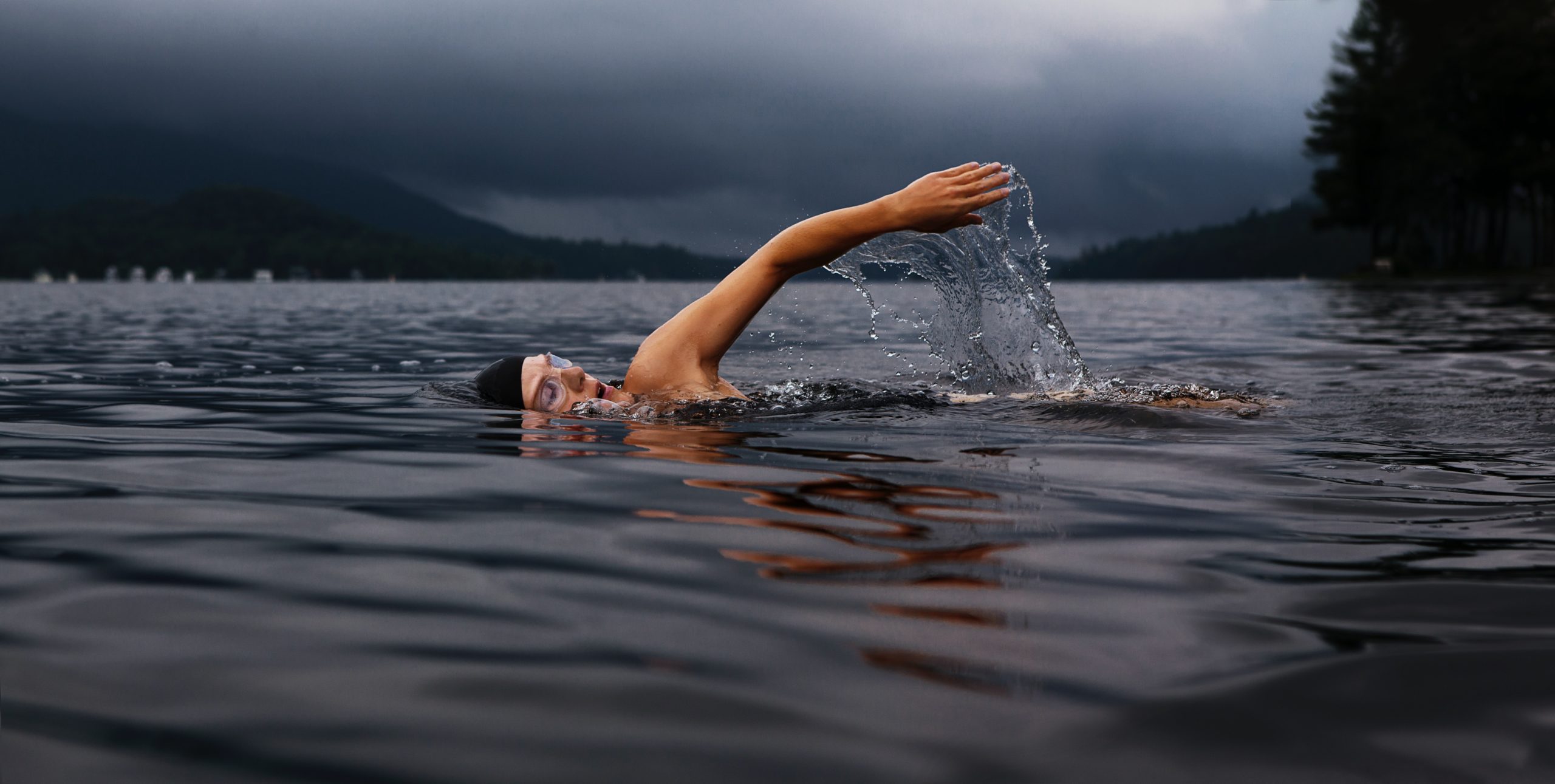
Do rhythmic melodies help you train more successfully? Or are extraneous sounds only distracting from sports? In this article, we have collected all the research on this topic. And we’ll tell you whether it is useful to study with music and how the tempo and meaning of the compositions affect our achievements.
It is known that musical accompaniment affects athletic performance. It is much more pleasant to train to your favourite tracks. It turns out that the role here is played not only by the motivating lyrics, but also by the instrumental part. How does music work?
Helps to speed up
Music can have a significant impact on the success of your workouts by helping to increase the pace of your exercise. This was proved by researchers from John Moores University, Liverpool, UK. They tracked people who exercised on exercise bikes. Unbeknownst to them, scientists accelerated or slowed down the music in the gym. The subjects immediately, as if on command, began to pedal a little faster or a little slower.
A similar result was obtained by the authors of another study. They invited volunteers to work out with a 25-minute playlist of 6 popular youth tracks. The sound speed was also imperceptibly changed by 10% without changing the pitch. At first, the participants in the experiment trained under the usual version. Then under accelerated, and finally – under slowed down. None of them noticed the difference. However, the fact that changing the tempo of the music forces people to move faster or slower has been confirmed.
Something new also came to light. The subjects noted that it was more pleasant to train with the fast version. Although they put in more effort, they did not feel any discomfort from it. Researchers hypothesized that bouncy compositions not only motivate more active workouts, but also distract from unpleasant sensations, helping to cope with physical activity more easily.
Dulls fatigue
Listening to music interferes with the signals of fatigue that the muscles send to the brain. Scientists from the University of Washington were able to confirm this in 2007. Participants in the experiment who listened to music or watched a movie during training noted that they were less tired than those who exercised without such support.
Before that, experts have already studied how athletes feel when they train in complete silence or darkness. It turned out that earplugs or a blindfold contributed to more exercise discomfort. Scientists believe this is due to the fact that the brain cannot concentrate on signals from all senses at the same time. When a person is fascinated by a movie or favourite song, they may not feel tired longer. And when there is nothing to be distracted by, all the unpleasant sensations become many times stronger.
Increases concentration and maintains pace
Fast tracks have been proven to increase endurance, while motivating lyrics help you withstand the stress of strength training. However, this does not mean that in order to obtain better sports results, it is worth training to absolutely any music. There are no universal tracks. According to experts from the Brunel University of London, psychosocial factors play a huge role in this.
The reaction of the audience is determined by four components, scientists are sure. In addition to the rhythm of the composition, its melody is important, what associations it evokes in a person and how it affects him. Therefore, the most effective for training will be your own playlist, compiled taking into account individual preferences.
This was confirmed by an experiment by sports physicians from McMaster University in Hamilton, Canada. 20 people were invited to take part in it, who had never been involved in athletics before. Participants with connected heart monitors pedaled exercise bikes for 30 seconds, then rested for one minute. After several approaches, the researchers recorded the readings of the instruments.
At the next stage, the volunteers trained with their own playlists with their favorite music. After that, the scientists re-examined the data of cardiac monitors and exercise bikes, and also asked the subjects about their subjective feelings from training. They admitted that they were less tired during the second stage than at the beginning. And the displays of the simulators showed that they covered a greater distance at a higher speed. So there was an assumption that “own” music significantly increases concentration and helps to adhere to a certain tempo.
And what about movies and TV shows?
Contrary to expectations, video accompaniment, on the contrary, degrades performance. A number of studies have confirmed that exercise only slows down when you watch your favorite TV show. Scientists believe this is due to the fact that this way a person is distracted much more than necessary. He not only stops feeling tired, but also does not notice that he is making less effort.
After all, watching video requires more attention than listening to audio. In addition, a person needs to keep his head in an uncomfortable position. Music is more useful because it has a certain rhythm to which you can adjust. This is not the case with cinema.
However, everything is individual. And each has its own motivation. If the opportunity to watch a new episode of the series motivates you to study more often, it’s still good, experts sum up. After all, strength and endurance primarily depend on how often you go to the gym, how much time you devote to exercise. Therefore, study how you are feeling determine what it is better for you to train listening rhythmicalwork out
playlist or an interesting movie.